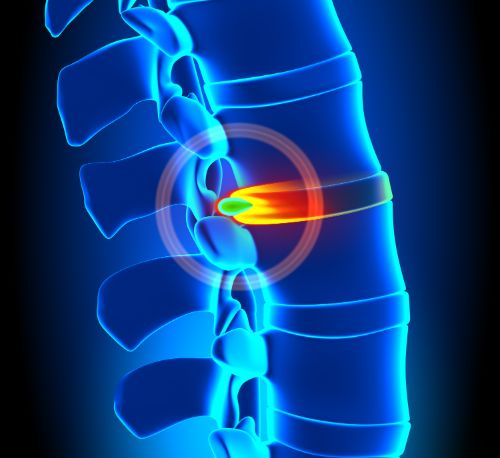
“Disc herniation” is a term that is commonly used in describing spinal pain or sciatica. However, when asked, most patients don’t understand what the term means. We’re going to briefly describe what a disc herniation is and how it can cause pain.
- The disc is a cushiony structure that sits between the vertebra.
- The disc cushions the spine and contributes to the stability of the spine.
- The disc consists of a fibrous band surrounding a gelatinous like filling.
- The fibrous band of the disc can tear as a result of the normal aging process and physical stressors, like over-exertion or an accident.
- When the fibrous band tears and the central disc material escapes into the fibrous band a herniation occurs.
- The herniation might only involve the inner portion of the fibrous band and results in a smooth broad protuberance of the normal disc. This is called a contained disc herniation. This is also commonly called a disc “bulge.”
- When the herniation results in a focal and discreet protrusion of the normal disc contour, it is referred to as a “focal disc protrusion.”
- The outer disc fibrous band contains nerves. Therefore, a rip in the disc fibrous band can be painful. This is especially so with bending and sitting, since these positions place pressure on the rear of the disc where herniations more commonly occur.
- Disc herniations can cause pain by protruding so much that they place pressure on spinal nerves. This can cause limb pain, numbness or even limb weakness.
- Disc herniations can also cause pain by producing inflammation. The disc material is normally walled off by the fibrous band. When the band rips, the disc material causes swelling and inflammation of the disc.
- Removing the herniated portion of disc can relieve pain by reducing inflammation and reducing pressure on nearby nerves.